6.2.4.4 Packet Tracer – Router and Switch Resilience Answers Packet Tracer – Router and Switch Resilience (Answers Version) Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only. Addressing Table Device IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Site HQRouter 10.44.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Metropolis Bank HQ Objectives Part 1: Continue reading. Mar 15, 2018 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks (Answer Version) Answer Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answer copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Switch Port VLAN PC1 NIC 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 S2 F0/11 10 PC2 NIC 172.17.20.22 255.255.255.0 S2 F0/18 Continue reading. CCNA 2 Lab: 3.2.2.4/6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Trunks Instructions Answers file completed free download.pdf file Answers 100%. May 30, 2019 Download Cisco Packet Tracer Version 6.2. Windows Linux. How Can I Download Cisco Packet Tracer 6.2 on My Device? Download Cisco Packet Tracer 6.2 on your device. As soon as it downloads, then let it install on your computer. When it’s installed, then launch it. Complete the on-screen instructions to get access to it. 6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks (Answer Version) Answer Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answer copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Switch Port VLAN PC1 NIC 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 S2 F0/11 10 PC2 NIC 172.17.20.
- Packet Tracer 6.2.2.4 Configuring Eigrp
- 6.2 2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Trunks Instructions Answers
6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks
Packet Tracer – Configuring Trunks (Answer Version)
Answer Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answer copy only.
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Switch Port | VLAN |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.17.10.21 | 255.255.255.0 | S2 F0/11 | 10 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.17.20.22 | 255.255.255.0 | S2 F0/18 | 20 |
| PC3 | NIC | 172.17.30.23 | 255.255.255.0 | S2 F0/6 | 30 |
| PC4 | NIC | 172.17.10.24 | 255.255.255.0 | S3 F0/11 | 10 |
| PC5 | NIC | 172.17.20.25 | 255.255.255.0 | S3 F0/18 | 20 |
| PC6 | NIC | 172.17.30.26 | 255.255.255.0 | S3 F0/6 | 30 |
Objectives
Part 1: Verify VLANs
Part 2: Configure Trunks
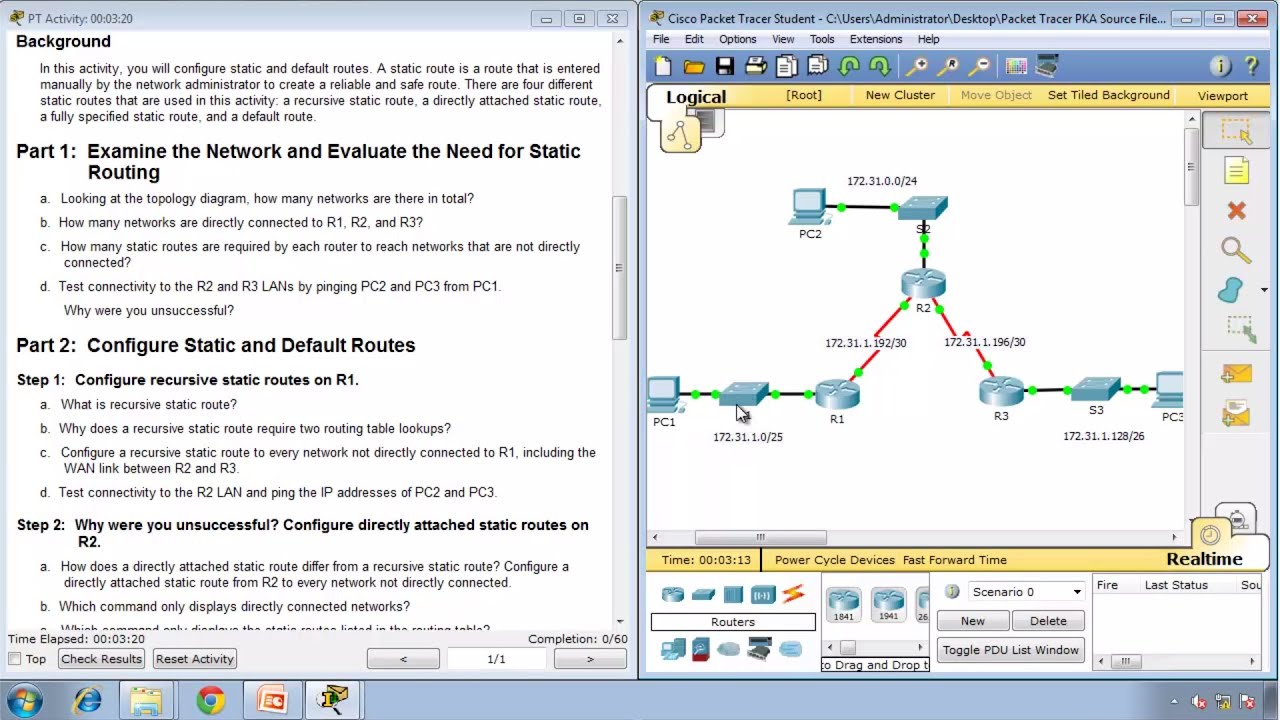
Background
Trunks are required to pass VLAN information between switches. A port on a switch is either an access port or a trunk port. Access ports carry traffic from a specific VLAN assigned to the port. A trunk port by default is a member of all VLANs; therefore, it carries traffic for all VLANs. This activity focuses on creating trunk ports, and assigning them to a native VLAN other than the default.
Part 1: Verify VLANs
Step 1: Display the current VLANs.
- On S1, issue the command that will display all VLANs configured. There should be ten VLANs in total. Notice how all 24 access ports on the switch are assigned to VLAN 1.
- On S2 and S3, display and verify all the VLANs are configured and assigned to the correct switch ports according to the Addressing Table.
Step 2: Verify loss of connectivity between PCs on the same network.
Although PC1 and PC4 are on the same network, they cannot ping one another. This is because the ports connecting the switches are assigned to VLAN 1 by default. In order to provide connectivity between the PCs on the same network and VLAN, trunks must be configured.
Part 2: Configure Trunks
Step 1: Configure trunking on S1 and use VLAN 99 as the native VLAN.

- Configure G0/1 and G0/2 interfaces on S1 for trunking.
- S1(config)# interface range g0/1 – 2
- S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
- Configure VLAN 99 as the native VLAN for G0/1 and G0/2 interfaces on S1.
- S1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99
- The trunk port takes about a minute to become active due to Spanning Tree. Click Fast Forward Time to speed the process. After the ports become active, you will periodically receive the following syslog messages:
- %CDP-4-NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Native VLAN mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet0/2 (99), with S3 GigabitEthernet0/2 (1).
- %CDP-4-NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Native VLAN mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet0/1 (99), with S2 GigabitEthernet0/1 (1).
- You configured VLAN 99 as the native VLAN on S1. However, S2 and S3 are using VLAN 1 as the default native VLAN as indicated by the syslog message.
- Although you have a native VLAN mismatch, pings between PCs on the same VLAN are now successful. Why? Pings are successful because trunking has been enabled on S1. Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) has automatically negotiated the other side of the trunk links. In this case, S2 and S3 have now automatically configured the ports attached to S1 as trunking ports.
Step 2: Verify trunking is enabled on S2 and S3.
On S2 and S3, issue the show interface trunk command to confirm that DTP has successfully negotiated trunking with S1 on S2 and S3. The output also displays information about the trunk interfaces on S2 and S3.
Which active VLANs are allowed to cross the trunk? 1, 10, 20, 30, and 99.
Step 3: Correct the native VLAN mismatch on S2 and S3.
- Configure VLAN 99 as the native VLAN for the appropriate interfaces on S2 and S3.
- Issue show interface trunk command to verify the correct native VLAN configuration.
Step 4: Verify configurations on S2 and S3.
- Issue the show interface interface switchport command to verify that the native VLAN is now 99.
- Use the show vlan command to display information regarding configured VLANs. Why is port G0/1 on S2 no longer assigned to VLAN 1? Port G0/1 is a trunk port and trunks ports are not displayed.
Packet Tracer 6.2.2.4 Configuring Eigrp

Suggested Scoring Rubric
6.2 2.4 Packet Tracer Configuring Trunks Instructions Answers
Packet Tracer scores 80 points. The three questions in Step 1, 2 and 4 are worth 20 points.